Table Of Content
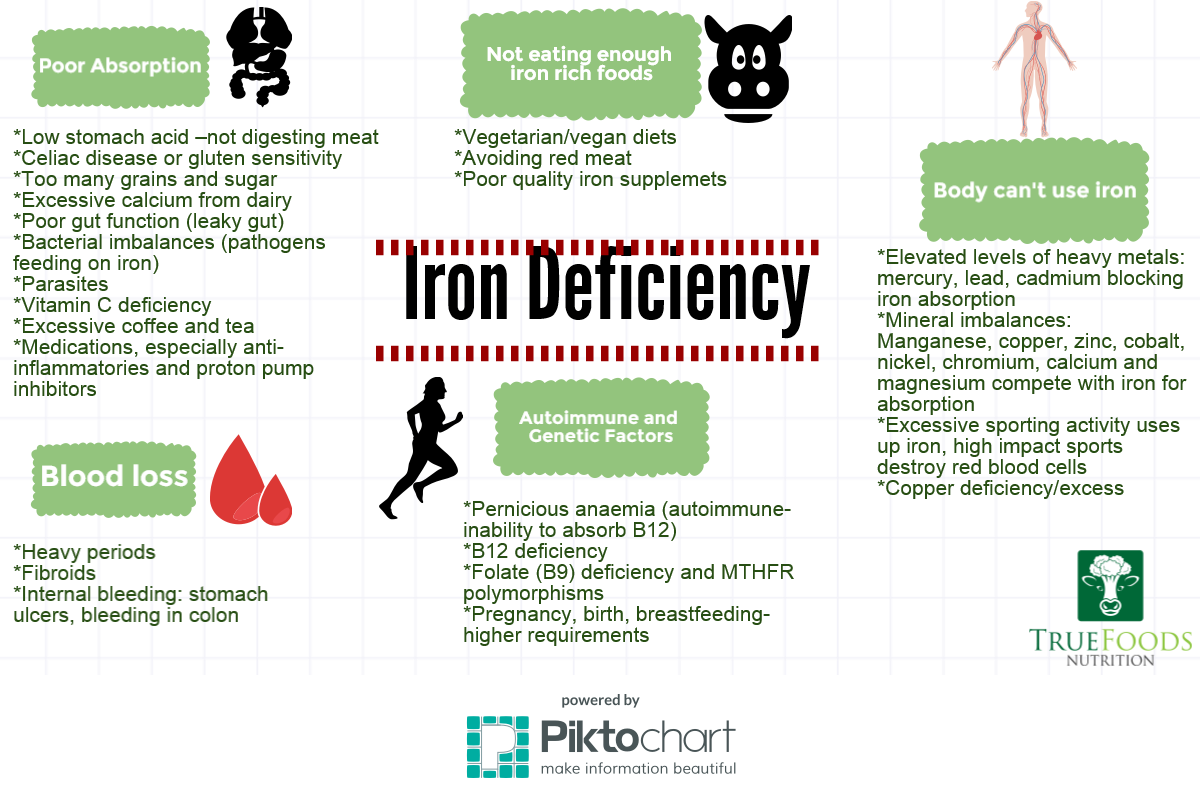
This may occur from an all-around poor and not well-balanced diet, or not planning enough iron-rich foods into a vegetarian or vegan lifestyle. Often, this scenario may be easily remedied by just making sure to insert more iron-rich foods into your meals, which can be done using either animal or plant sources. Finally, there may be a connection between women with low iron levels and a condition called telogen effluvium, which causes a reversible, but sudden shedding of a significant amount of your hair.
vitamin B7 (biotin)
In this review we summarize the role of vitamins and minerals, such as vitamin A, vitamin B, vitamin C, vitamin D, vitamin E, iron, selenium, and zinc, in non-scarring alopecia. Hair loss is a common problem that may be improved with vitamin and mineral supplementation. Vitamins and minerals are important for normal cell growth and function and may contribute to hair loss when they are deficient.
Practical pointers about protein
It would appear that the prevalence of reduced ferritin levels (below 30–40 ng/dL) is higher among women with diffuse hair loss than among women in the general population. Ferritin levels below 30 ng/dL were found in 40–50% of the women in Denmark and Norway [34], 32% of the women in Portugal [35], and 47% of the women in Cambodia [38]. If your doctor thinks iron deficiency anaemia might be behind your hair loss, they’ll first carry out a blood test, which looks for levels of a protein called ferritin.
Associated Data
While supplementation is relatively affordable and easily accessible, it is important to know which vitamins and minerals are helpful in treating hair loss. However, raising ferritin levels will not increase hair growth in healthy individuals who have normal iron and ferritin levels. When a doctor diagnoses low ferritin levels, they will typically advise the person to adjust their diet and take an iron supplement until iron levels normalize.
If your healthcare provider doesn't suspect GI blood loss, you may need to start a trial of iron supplements with close follow-up. If there is no improvement after a few weeks or if it's still unclear what is causing your anemia, you may need iron studies. A complete blood count (CBC) is a blood test that counts your platelets and your red and white blood cells. This test can only suggest iron deficiency anemia, because there are also other causes. Your healthcare provider will try to identify the cause based on your medical history and exam. However, it is important to always include your doctor in the decision to supplement with iron, as too much iron can cause dangerously high levels and be an even worse problem if not done correctly.
If the hair loss is directly related to low iron and ferritin levels, then theoretically, increasing iron intake should replenish the ferritin in the hair follicles, leading to healthier hair. There are many causes of hair loss in both women and men, so if you’re concerned about it, your first step should be booking an appointment with a doctor to discuss your options. Additional research suggests an iron deficiency may cause hair similar to the pattern seen in androgenic alopecia––the most common type of hair loss. Often called male pattern baldness, androgenic alopecia can affect anyone. For men, it’s usually a receding hairline or bald spot on the crown of the head.
Use straighteners and hair curlers that emit a lot of heat sparingly. With a combo of this and an iron-rich diet, you’ll be on your way to healthier hair. For men and postmenopausal women, gastrointestinal blood loss (which can occur from conditions like ulcers, Crohn’s disease, and celiac disease) is a leading cause of low iron. People living with kidney failure or who practice a vegan diet may also be more prone to iron deficiencies.

Other non-hormonal tests include cardiac and tumor markers, infectious disease serologies, biomarkers of anemia and autoimmune diseases, and concentrations of immunosuppressive drugs [29–32]. Consumption of vitamin A exceeding the recommended daily limit of approximately 10,000 IU a day can lead to vitamin A toxicity. In a case report, a 60-year-old male who had been taking excess vitamin A supplements experienced non-scarring fronto-central alopecia as well as decreased pubic and axillary hair. The patient also reported dystrophic nail changes and an erythematous rash. Taken together, these changes were concurrent with drug toxicity that aligned with the patient’s over-consumption of vitamin A [21].

stress
The authors hypothesized that iron deficiency might change the normal progression of the hair cycle. However, whether these six genes play a role in iron-dependent processes in the hair follicle remains to be elucidated. Although not yet proven, there is a prevailing view that hepcidin upregulation diverts iron from the hair follicle to support the essential iron requirements.
Hair loss has many causes, and it can affect adults and children of all genders. When you don’t have enough iron, your body can’t produce the hemoglobin in your blood. Hemoglobin carries oxygen for the growth and repair of cells in your body, including the cells that stimulate hair growth. People experiencing female pattern baldness may also notice a general thinning of hair on the top of your head, but hair loss typically won’t occur on the front of your scalp, per Harvard Health.
Alopecia areata (AA) occurs when the immune system attacks the hair follicle. Studies have shown a relationship between AA and low vitamin D levels. However, more studies are needed to determine the effect of iron and zinc supplementation on AA patients.
We recommend screening for these vitamins and minerals in patients presenting with premature graying of hair and subsequent supplementation of the deficient micronutrients [114]. Genetic causes of biotin deficiency can be either neonatal or infantile. The neonatal type is a life-threatening condition manifested during the first 6 weeks of life, and it is due to a holocarboxylase enzyme deficiency. It is usually manifested with severe dermatitis and alopecia, where there is loss of vellus and terminal hair on the scalp; eyebrows, eyelashes, and lanugo hair can also be absent. The infantile form of biotin deficiency occurs after 3 months of delivery and is due to a lack of the enzyme called biotinidase.
Too much iron in the body may lead to serious issues in the liver and other organs. Of these, 6,641 suffered from alopecia and 3,388 were in the control group. Every article on Health Guide goes through rigorous fact-checking by our team of medical reviewers. Our reviewers are trained medical professionals who ensure each article contains the most up-to-date information, and that medical details have been correctly interpreted by the writer.
Your genes, hormonal changes, illness, and even stress can come into play. And while iron deficiency could be at the root of your problem, if you're experiencing hair loss, your best bet is to see a dermatologist. They can perform tests to determine the cause, and if they suspect iron loss, they'll order labs to find out. Pregnancy might see it get better, whereas once you give birth, it may worsen. "Postpartum hair loss is a frequent dermatologic concern and, as one may expect, may impact self-confidence and mental state," Weimann explains.
If you’re unsure about the right amount of iron to take, speak to a pharmacist or doctor. The average recommended daily amount of iron for men 18 and above is around 8.7mg. As women are more prone to iron deficiency, it’s recommended that they aim for about 14.8mg a day until the age of 50, and 8.7mg in the years after. There is some evidence that iron deficiency and anaemia are linked to hair loss, however, it’s not thought to be a common symptom. Gradually thinning hair as you age is also normal, and largely hereditary. But hair loss—especially when it's sudden or at a young age—can also be a sign of certain medical conditions or nutrient deficiencies.

No comments:
Post a Comment